Data flow: Accessing content, applications, and public Internet destinations using Safe Mode
This data flow describes how data travels between devices and a public Internet destination using Safe Mode. With Safe Mode,
CylanceGATEWAY
blocks apps and users from accessing potentially malicious destinations and enforces an acceptable use policy (AUP) by intercepting DNS requests. The CylanceGATEWAY
cloud services evaluate each DNS query against the configured ACL rules and network protection settings, and then instructs the agent to allow or block the request in real time. If allowed, the DNS request completes normally over the bearer network. Otherwise, the CylanceGATEWAY
agent overrides the normal response and prevents access. 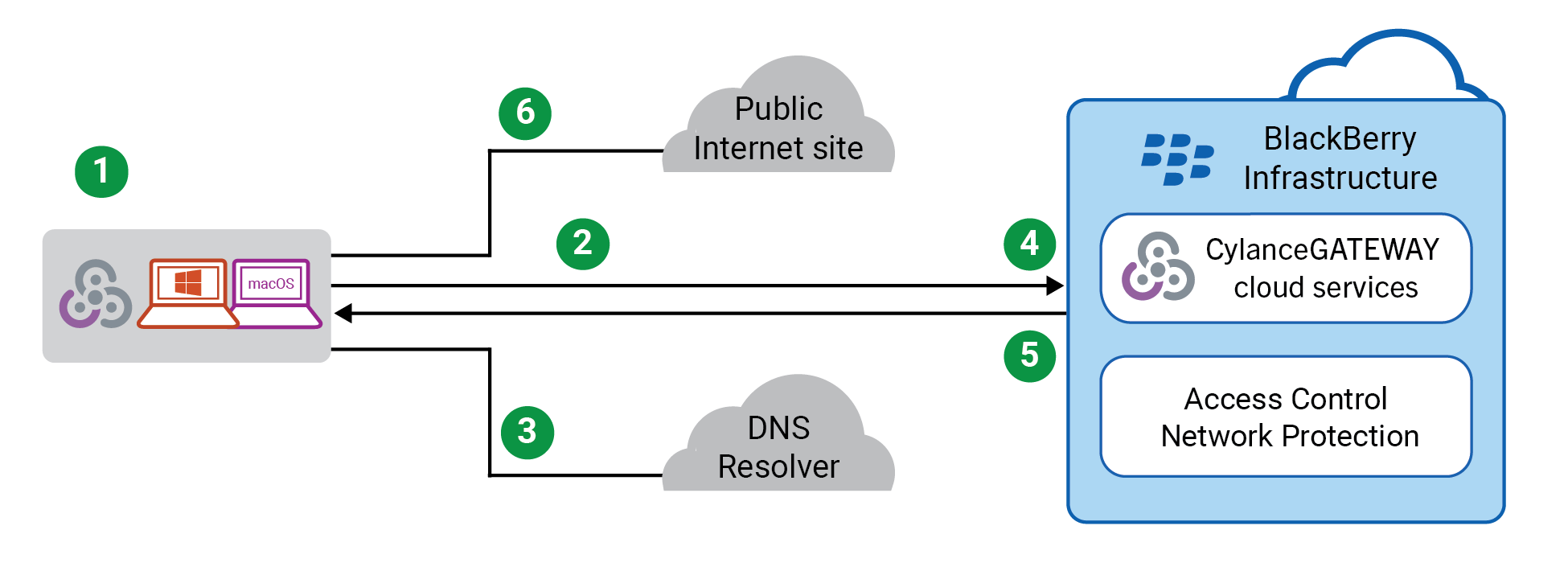
The above diagram shows the following sequence.
- TheCylanceGATEWAYagent has Safe Mode enabled and the user attempts to access an Internet destination.
- TheCylanceGATEWAYagent intercepts the DNS request that is made from the device and queries theCylanceGATEWAYcloud services with information from that request.
- The agent proxies the DNS request to the original DNS server.
- TheCylanceGATEWAYcloud services evaluate each query against the configured ACL rules and network protection settings, and then instructs the agent to allow or block the request.
- If access is allowed, the agent proxies the original DNS server's response back as the response to the original DNS request. Otherwise, the agent injects a DNS response that blocks access.
- The agent uses the results of an allowed DNS request to access an Internet destination.