- Configuring BlackBerry UEM for the first time
- Changing BlackBerry UEM certificates
- Configuring BlackBerry UEM to send data through a proxy server
- Configuring connections through internal proxy servers
- Connecting to your company directories
- Configuring Microsoft Active Directory authentication in an environment that includes Exchange linked mailboxes
- Connect to a Microsoft Active Directory instance
- Connect to an LDAP directory
- Enable directory-linked groups
- Enabling onboarding
- Synchronize a company directory connection
- Removing a connection to a company directory
- Connecting to an SMTP server to send email notifications
- Configuring database mirroring
- Connecting BlackBerry UEM to Microsoft Azure
- Create a Microsoft Azure account
- Synchronize Microsoft Active Directory with Microsoft Azure
- Create an app registration in Azure
- Configuring Azure Active Directory conditional access
- Configure BlackBerry UEM as a Compliance Partner in Azure
- Configure Azure Active Directory conditional access
- Configure the BlackBerry Dynamics connectivity profile to support the Azure Conditional Access feature
- Assign the Feature - Azure conditional access app to users
- Configure a BlackBerry Dynamics Profile
- Remove devices from Azure Active Directory conditional access
- Enable access to the BlackBerry Web Services over the BlackBerry Infrastructure
- Obtaining an APNs certificate to manage iOS and macOS devices
- Configuring BlackBerry UEM for DEP
- Configuring BlackBerry UEM to support Android Enterprise devices
- Extending the management of Chrome OS devices to BlackBerry UEM
- Setting up management of Chrome OS devices if you have already configured BlackBerry UEM to use Android Enterprise
- Create a service account that BlackBerry UEM uses to authenticate with your Google Cloud or Google Workspace by Google domain
- Enable additional APIs to allow BlackBerry UEM to sync the Chrome OS data
- Integrate BlackBerry UEM with your Google Cloud or Google Workspace by Google domain so you can use Chrome OS devices
- Synchronize BlackBerry UEM with the Google admin console
- Simplifying Windows 10 activations
- Migrating users, devices, groups, and other data from a source server
- Prerequisites: Migrating users, devices, groups, and other data from a source server
- Connect to a source server
- Considerations: Migrating IT policies, profiles, and groups from a source server
- Migrate IT policies, profiles, and groups from a source server
- Complete policy and profile migration for BlackBerry Dynamics-activated users
- Considerations: Migrating users from a source server
- Migrate users from a source server
- Considerations: Migrating devices from a source server
- Migrate devices from a source server
- Migrating DEP devices
- Configuring BlackBerry UEM to support BlackBerry Dynamics apps
- Manage BlackBerry Proxy clusters
- Configure Direct Connect using port forwarding
- Configure BlackBerry Dynamics properties
- Configure communication settings for BlackBerry Dynamics apps
- Sending BlackBerry Dynamics app data through an HTTP proxy
- BlackBerry Dynamics connectivity and routing behavior
- Default routing
- Example routing scenarios
- Scenario 1: Route traffic to specific servers or domains through BlackBerry Proxy
- Scenario 2: Route all traffic through the BlackBerry Proxy and then through a web proxy server
- Scenario 3: Route some traffic internally for most apps but configure a proxy server specifically for web browsing using BlackBerry Access
- BlackBerry Dynamics data flow
- Configuring Kerberos for BlackBerry Dynamics apps
- Connect BlackBerry UEM to a BlackBerry Dynamics PKI connector
- Integrating BlackBerry UEM with Cisco ISE
- Requirements: Integrating BlackBerry UEM with Cisco ISE
- Create an administrator account that Cisco ISE can use
- Add the BlackBerry Web Services certificate to the Cisco ISE certificate store
- Connect BlackBerry UEM to Cisco ISE
- Example: Authorization policy rules for BlackBerry UEM
- Managing network access and device controls using Cisco ISE
Single-realm Kerberos environment
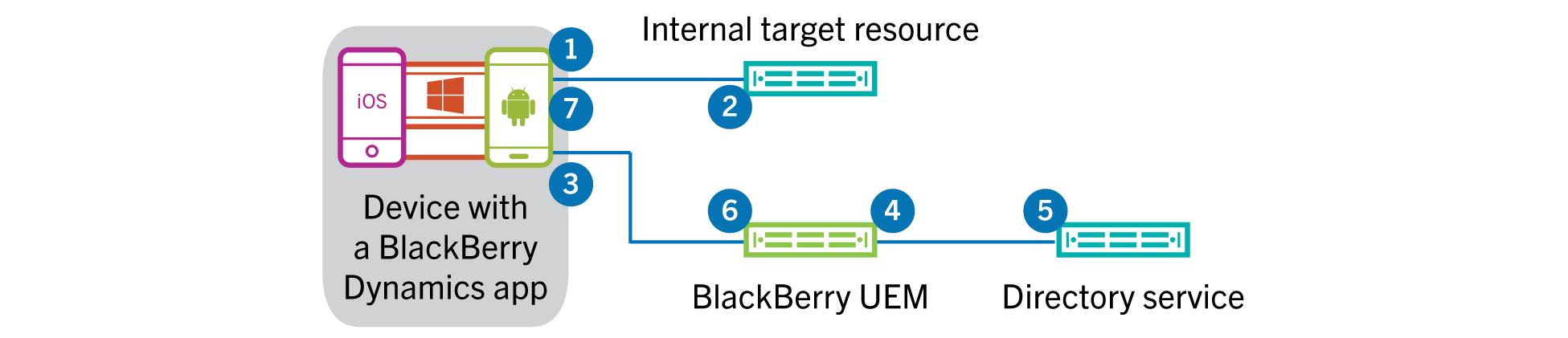
- ABlackBerry Dynamicsapp makes a request to an internal server or service (thetarget).The target can be either a host name (server name) or an account that is to be protected byKerberosandBlackBerry Dynamics. For example, if IIS is running on a server as the Network service, the target is the server running IIS as Network. On the other hand, if IIS is running as a user (for example, IISSrvUser), then the target is that user name, IISSrvUser.
- The target replies with an authentication challenge thatBlackBerry Dynamicsintercepts.
- TheBlackBerry DynamicsSDK sends a request toBlackBerry UEMfor a service ticket to access the target.
- BlackBerry UEMauthenticates the user or app (through internalBlackBerry Dynamicsprotocols) and asks for a service ticket on behalf of the user (delegation) for the service on the target.
- Active Directorychecks its local policy. If the user has permission to access the resource on the target and if the resource on the target is allowed (constrained),Active Directoryreturns toBlackBerry UEMa service ticket for the resource.
- BlackBerry UEMsends the necessary information from the returned service ticket to theBlackBerry DynamicsSDK.
- TheBlackBerry Dynamicsapp uses the information fromBlackBerry UEMto complete the authentication to the target.