Data flow: Receiving configuration updates on an iOS device
iOS
device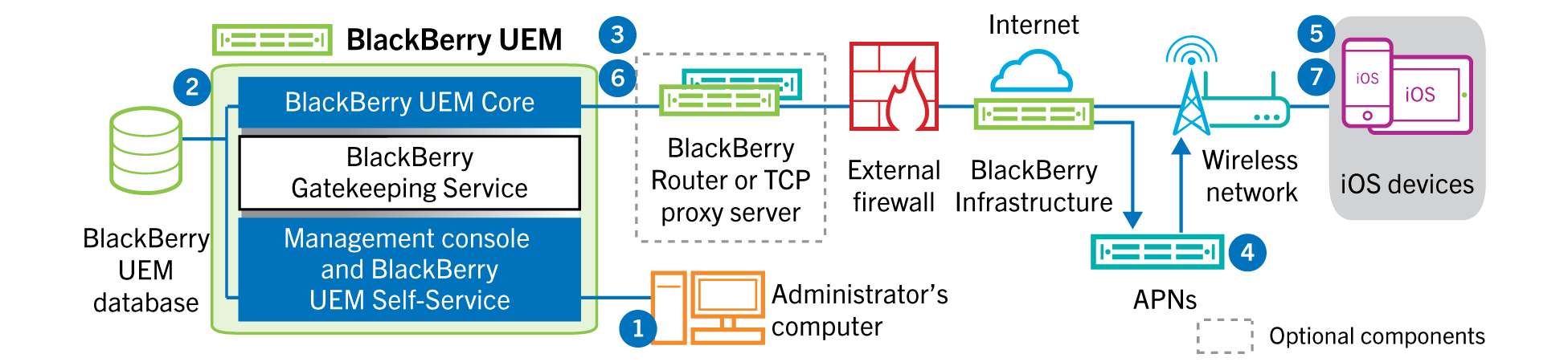
- An action is taken in the management console that triggers a configuration update for aniOSdevice. For example, you update the IT policy or assign a new profile or app to the user account.
- Updates are applied inBlackBerry UEMand objects that must be shared with the device are identified.
- TheBlackBerry UEM Coreperforms the following actions:
- Contacts theBlackBerry Infrastructure, through theBlackBerry Routeror TCP proxy server, if installed, and the external firewall over port 3101.
- Sends a request through theBlackBerry Infrastructureto the APNs to notify the device that an update is pending.
- The APNs sends a notification to the native MDM Daemon on theiOSdevice to contact theBlackBerry UEM Core.
- When the native MDM Daemon on theiOSdevice receives the notification, it contacts theBlackBerry UEM Core, on port 3101 on the external firewall, passing through theBlackBerry Routeror TCP proxy server, if installed, to retrieve any pending actions.
- TheBlackBerry UEM Corereplies with the highest priority action. Priority is given to device actions, such as Delete device data and Lock device. TheBlackBerry UEM Coresends only one command at a time. If necessary, additional information is included in the response. If no actions or commands are pending for the device, theBlackBerry UEM Corereplies to the device with an idle command.
- The native MDM Daemon on theiOSdevice performs the following actions:
- Inspects the response from theBlackBerry UEM Core, schedules the command to be processed, and waits for the command to run.
- Sends a response to theBlackBerry UEM Coreto update the command status. The status indicates whether the command ran successfully and provides an error message in the event of a failure.
Steps 6 and 7 are repeated until no more pending actions or commands must be performed on the device.